Federation Assurance Standard V1 March 2021
Return to Evidence of Identity Standard
This information is an archival record and is retained for reference purposes only.
You can access the latest version at Federation Assurance Standard – digital.govt.nz
This standard provides additional controls for parties that provide credentials on which others rely.
Application of this standard
This standard applies to any Credential Provider (CP). The CP is accountable for the controls stated in this standard, even if they have employed or contracted aspects to other parties.
Application of the controls in this standard will contribute to the reduction of identity theft, entitlement fraud, misrepresentation of abilities and the impacts that result.
The scope of the requirements in this standard is explicitly related to the identification aspects of federation. It does not include considerations for security, other implementation matters or any contractual agreements.
Effective date
This standard was effective from 1 March 2021, and has now been replaced by a newer version.
Scope
This standard applies whenever an individual, organisation or group wants to establish a Credential that can be reused by Entities in identification processes with multiple Relying Parties.
To enable Credentials to be reliably used in this way requires the development of some common agreements, which is why these Credentials are referred to as federated credentials. The standard does not cover the nature of these agreements but provides identification requirements for service providers wishing to become Credential Providers.
In relation to the scope of Identification management, this standard relates to the role of the Credential Provider and the establishing, presentation, facilitation and management of a Credential.
Diagram 1: Relationship between elements
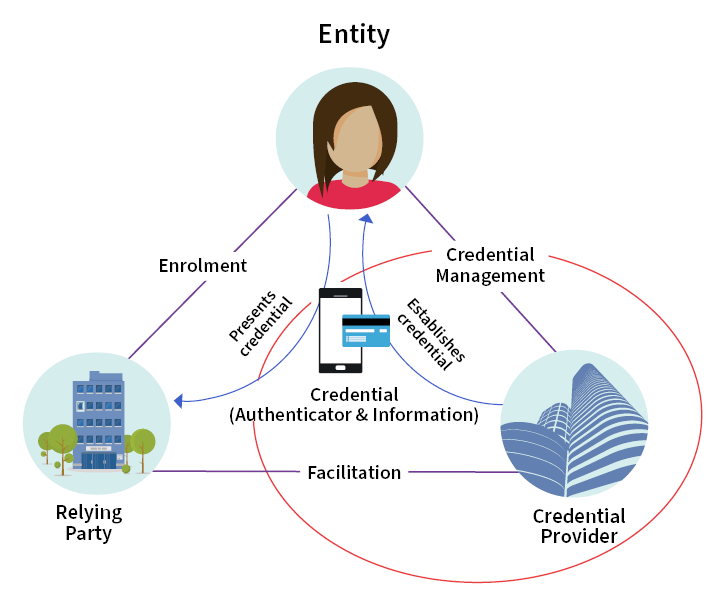
Detailed description of the image
This diagram shows a triangle representing the connections between Entities, Relying Parties, Credentials and Credential Providers.
At the top of the triangle is an Entity (in this example, a person). At the lower left of the triangle is a Relying Party (in this example a building representing an organisation). At the lower right of the triangle is a Credential Provider (in this example a different building representing an organisation).
At the centre of the triangle is a Credential (in this example represented by a mobile device and an access card).
The connection between Entity and Relying Party is labelled Enrolment. The connection between Entity and Credential Provider is labelled Credential Management. The connection between Relying Party and Credential Provider is labelled Facilitation.
There is a red cricle around Credential Provider, Credential Management and all the connections relating to these, to indicate the scope of this standard.
Relationship with other identification management standards
Assurance components
Table 1 describes each of the assurance components and the processes they relate to. A separate standard has been developed for each component. This standard addresses the last of these assurance components — Federation Assurance.
| Assurance component | Description |
|---|---|
|
IA Information Assurance |
Robustness of the process to establish the quality and accuracy of Entity Information. |
|
BA Binding Assurance |
Robustness of the process to bind the Entity to Entity Information and/or Entity to Authenticator. |
|
AA Authentication Assurance |
Robustness of the process to ensure an Authenticator remains solely in control of its holder. |
|
FA Federation Assurance |
Additional steps undertaken to maintain the integrity, security and privacy of a credential used in many contexts. |
Before applying this standard
Credentials
In this standard Credentials contain and make use of 3 aspects of information:
- Credential subject information — this is information that the holder of the credential, is overtly aware of making available to a Relying Party for their decision making.
- Presentation information — this is information (including metadata) and associated processes that support the trust and operation of the Credential (for example document security features, encryption, certificates).
- Facilitation information — this is information (including metadata) that is made available when the Credential Provider is involved in facilitating the presentation of the Credential to the Relying Party (for example references, timestamps, transaction identifiers, logs).
At a minimum a Credential consists of an Authenticator and Presentation information. Most Credentials have additional Credential subject information that determines its use for specific purposes. For example, to travel or to drive.
A Credential ‘holder’ refers to the individual Entity with whom a Credential was first established; the rightful holder.
Credential presentation
As Credentials evolve they are likely to contain larger amounts of Credential subject information that can be made available to Relying Parties. This reflects the need to better serve the individual Entities that hold them, especially as we move to more digital and remote service delivery.
To maintain the privacy of the holder, not all the Credential subject information in a Credential needs to be made available to a Relying Party. There are 2 forms of limitation:
- Partial presentation – a subset of the Credential subject information is made available to the Relying Party.
- Derived value presentation – one or more of the values in the presentation are deduced or inferred from the value in the Credential. For example, age can be inferred from a date of birth.
Providing and facilitating the presentation of a Credential can involve 1 or more parties working together. Other standards and jurisdictions segment these using terms such as Information Provider, Attribute Provider, Credential Service Provider, Verifier. Regardless of the number of Parties that are working together, the Credential Provider is the accountable party for the purposes of maintaining trust.
Document structure
This standard divides requirements into 2 sections:
- Requirements for providing a credential service — preparatory (general) controls
- Requirements for credential presentation — controls that apply to presentation instances.
Assumptions
The following assumptions have been made:
- Presentation of a Credential does not necessarily require the involvement (facilitation) of the Credential Provider.
- There are many ways in which a Credential can be presented, including physically or digitally and whether all or only part of the Credential subject information is made available.
Requirements for providing a credential service
The requirements in this section apply before any Entity enrols for a Credential.
The Credential Provider will apply the Information Assurance, Binding Assurance and Authentication Assurance Standards during the enrolment process.
Objective 1 — Credential federation risk is understood
Rationale
For holders to trust their Credential is being adequately protected from unauthorised access and use, the risk the Credential poses needs to be understood.
Obtaining and using a federated Credential has the potential to expose holders to additional risks arising from increased collection of information.
As Credentials move from narrow purposes with minimal attributes to ones that can fulfil several identification requirements, care needs to be taken with the accumulation of information. This includes the attributes that are contained in the Credential regardless of any limitation made during presentation.
Credential Providers may also need to achieve specific levels of assurance determined by contracts and/or legislation.
FA1.01 Control
The CP MUST carry out an assessment of the risk posed by the existence of the federated Credential before offering it.
Additional information — While any risk assessment process can be used, specific guidance is available on Assessing identification risk.
FA1.02 Control
The CP MUST evaluate the risk of all information available to a holder viewing or managing their credential and apply the corresponding level of authentication.
Additional information — Where credentials can be presented in privacy-centric ways using partial presentation and derived values, the authentication level for presentation may be lower than that needed for Credential management.
Objective 2 — Credentials have recognised levels of assurance
Rationale
Consistent approaches to Credential establishment and an ability for Relying Parties to know the Credential and the Credential Provider are genuine, reduce the likelihood Credentials will be able to be used as avenues for identity theft and fraud.
As more Credentials become able to be used for multiple purposes, Entities can also use assurance levels to select Credentials best suited to the identification needs of the services they most commonly use.
FA2.01 Control
The CP MUST establish the Credential using identification processes that comply with the latest versions of the following standards:
- Information Assurance Standard
- Binding Assurance Standard
- Authentication Assurance Standard.
Additional information — The level to which assurance has been gained against the above standards will determine the levels to be declared in FA6:01.
FA2.02 Control
The CP MUST provide mechanisms, consistent with the intended assurance level, that enable the Credential to be recognised as bona fide.
FA2.03 Control
The CP MUST provide mechanisms, consistent with the intended assurance level, that enable the Credential Provider to be recognised as bona fide.
Objective 3 — Participation activity cannot be correlated
Rationale
Federation of Credentials offers numerous benefits to Entities. Obtaining and using a federated Credential has the potential to expose Entities to additional risks arising from the capability to track and profile.
A holder using the same Credential multiple times potentially enables the Credential Provider and Relying Parties to build a profile of the holder’s transactions. The availability of such data makes it vulnerable to uses that may not be anticipated or desired by the holder and could inhibit adoption of federated services.
FA3.01 Control
The CP MUST NOT correlate, allow correlation or create profiles of a holder’s information or activity.
FA3.02 Control
The CP MUST reduce the ability for Relying Parties to correlate holders by not including the holder’s unique Entity Information identifier as part of a Credential.
FA3.03 Control
The CP MUST reduce the ability for Relying Parties to correlate holders by not providing a single Credential identifier to multiple Relying Parties, where presentation of the Credential allows.
Additional information — Providing each Relying Party with a different identifier for the holder prevents correlation between Relying Parties but will still allow a single Relying Party to track the activity of 1 holder within its context.
FA3.04 Control
The CP SHOULD allow anonymity of the holder by not providing any persistent identifiers, where the context is appropriate, and the Credential presentation allows.
Objective 4 — Participation is inclusive
Rationale
Each Credential will have a purpose and corresponding holders who need to have them. Credential Providers have obligations including responsibilities under the Treaty of Waitangi and digital inclusion to ensure that Entities can participate on an equal footing. Therefore, consideration of the population of Entities who will depend on the Credential, is essential so as not to contribute to the exclusion of participation by any group.
FA4.01 Control
The CP MUST identify the population of Entities who will require the credential.
FA4.02 Control
The CP MUST support any Entity within the identified population to become a Credential holder.
Objective 5 — Credential is maintained
Rationale
Once a Credential is established there are several activities that maintain its relevance and integrity.
Some of these activities relate to managing the life cycle of the Credential such as updating, suspending and revoking the Credential.
Other activities enable fraud detection, for example, if interactions with Credentials are not logged and monitored, Credential Providers will not be able to appropriately prevent or investigate any misuse or compromise.
FA5.01 Control
The CP MUST provide the means for the Credential subject information contained in the Credential to be updated, by either:
- enabling Credential subject information in the Credential to be changed; or
- replacing the Credential; or
- establishing synchronous links to maintained sources of Credential subject information.
FA5.02 Control
The CP MUST provide the means for the holder to cancel a Credential or report its loss or compromise.
FA5.03 Control
The CP MUST provide (either directly or through a third party) support services to a holder whose Credential has been compromised.
FA5.04 Control
The CP MUST provide mechanisms for addressing holder complaints or problems arising from Credential establishment and presentation.
FA5.05 Control
The CP MUST provide mechanisms for addressing Relying Party complaints or problems arising from Credential presentation.
FA5.06 Control
The CP MUST be able to update the Credential status to prevent its use, even if the responses to authentication challenges are successful, and can either:
- suspend the Credential, allowing for recovery in the future; or
- revoke the Credential, permanent disablement or deletion.
Additional information — If the holder has requested deletion of a Credential, consider suspending it for a period of 1 month before revoking to allow for recovery if needed.
FA5.07 Control
The CP SHOULD set an expiry on a Credential where the usage and risk indicates this to be desirable.
FA5.08 Control
The CP MUST log all activity within the system, including but not limited to:
- who did the action
- when the action occurred
- what the action was — create, read, update or delete
- what was changed by the action — before and after.
Additional information — For physical Credentials this activity is more likely to apply to any database that supports it than the Credential itself.
FA5.09 Control
The CP MUST obtain additional confidence in the integrity of the Credential by taking preventative measures including but not limited to:
- auditing logs
- monitoring activities for adverse behaviours
- undertaking counter-fraud measures.
Additional information — Refer to guidance on counter-fraud measures (under development).
FA5.10 Control
The CP MUST provide notifications to the holder that allow them to self-detect potential compromise, these can include but are not limited to:
- the last time the holder accessed their Credential (where applicable)
- any change made to the holder’s Credential.
Additional information — If the change is to contact information, notification needs to be to the pre-change or alternative contact.
Requirements for credential presentation
The requirements in this section apply to the presentation of a Credential to a Relying Party.
In some instances, the Credential Provider is not part of the presentation interaction and the control will not apply.
Objective 6 – Presentations are consistent and recognised
Rationale
For Relying Parties to trust the integrity of a Credential they need to know it has been established and presented in a consistent and recognised way.
This includes knowing the Credential and the Credential Provider are genuine and the levels of assurance it provides.
FA6.01 Control
The CP MUST make level/s of assurance for the Credential subject information available to the Relying Party.
Additional information — Level of assurance is an expression representing the assurance level achieved by each of the three elements: information, binding and authentication. There can be a separate expression for each attribute in the Credential subject information.
FA6.02 Control
Where a single level of assurance expression is provided for a Credential, the CP MUST declare the lowest levels achieved.
FA6.03 Control
The CP MUST make the following additional Presentation information available to a Relying Party, where the presentation of the Credential allows:
- Transaction identifier: A unique identifier for the presentation
- Issuance: A timestamp indicating when the Credential was established (updated).
- Expiration: A timestamp indicating when the Credential is expected to expire.
- Credential Provider identifier: An identifier for the member of a multi-party Credential Provider who is the accountable party.
- Credential validity: Information and/or mechanisms for determining the validity of the Credential.
- Audience identifier: An identifier for the Relying Party that requested the presentation
Additional information — Some Presentation information applies to the whole presentation, some to each value in the presentation.
Objective 7 — Presentations are privacy-centric
Rationale
Use of a Credential (presentation) should not expose any holder to a reduction in privacy by doing so. Active application of privacy principles such as data minimisation and consent contribute to good identification management practice and reduce identity theft and its impacts.
FA7.01 Control
The CP MUST ensure the holder has given consent to make available Credential subject information.
FA7.02 Control
The CP MUST enable the holder to remove Credential subject information, where the presentation of the Credential allows.
FA7.03 Control
The CP SHOULD enable the holder to provide 1 or more derived values based on Credential subject information, where the presentation of the Credential allows.
FA7.04 Control
The CP MUST only make available the Credential subject information that was requested by the Relying Party, where the Credential Provider is facilitating the process.
Additional information — The Relying Party can request a derived value from the Credential subject information, in which case the Credential Provider does not provide the full value.
FA7.05 Control
The CP SHOULD NOT provide Credential subject information to a Relying Party that cannot provide a purpose for collecting it, where the Credential Provider is facilitating the process.
FA7.06 Control
The CP MUST only release Presentation and Facilitation information that are applicable to the Credential subject information the holder has consented to be made available.
FA7.07 Control
The CP MUST not make available any identifiers in Credential subject information, Presentation or Facilitation information that override requests for pseudonymous and/or anonymous manners of presentation.
FA7.08 Control
The CP MUST take measures relevant to the delivery channel to ensure the information made available by the Credential is not observed or disclosed to an unauthorised entity during presentation.
Objective 8 — Presentation content is unaltered
Rationale
Once a Credential holder has consented to Credential subject information being made available to a Relying Party, they both need to be able to trust that the same information is received by the Relying Party.
FA8.01 Control
The CP MUST take measures relevant to the delivery channel to ensure the information made available by the Credential is not altered.
FA8.02 Control
The CP MUST establish secure communication channels between all parties, where more than 1 party is required to complete a process.
Additional information — This refers only where multiple parties are delivering the establishment and presentation of Credentials, not the Entity or the Relying Party.
Objective 9 — Presentation can be investigated
Rationale
An important element of trust in any identification process is the ability for an Entity or Relying Party to question a process or presentation. While various controls allow for anonymity, pseudonymity and blinding of various parties in the Credential presentation process, none of these should prevent the investigation of a suspicious transaction.
FA9.01 Control
The CP MUST make available contact information to holders and Relying Parties, for the purposes of initiating a query about a Credential or its presentation.
FA9.02 Control
The CP MUST collect the following information, where the presentation of the Credential allows:
- Transaction identifier: A unique identifier for the presentation event
- Timestamp: A timestamp of when the presentation occurred
- Holder identifier: An identifier for the Entity that the presentation is about
- Audience identifier: An identifier for the Relying Party intended to receive the presentation
- Credential subject information: Values and/or references that describe the Credential subject information that was presented
- Presentation Information: Information about the integrity mechanisms used
- Facilitation information: Values and/or references that describe the facilitation information that was exchanged.
What compliance means
In order to comply with this standard ALL the controls will be met.
Voluntary compliance by any Party wishing to follow good practice for contributing to the prevention of identity theft and fraud, will be by self-assessment.
Compliance with this Standard given through means such as contractual requirements, Cabinet mandate, legislation etc., will include mechanisms for assessment and certification.
Exemptions
Currently, no process exists by which a mandated organisation can secure an exemption from the requirement to meet this Standard.
Related advice
A companion implementation guide will be developed for this standard and published in Identification Management — Guidance
Contact
Department of Internal Affairs Te Tari Taiwhenua